 메뉴열기
메뉴열기
급성기 acute coronary syndrome (ACS) 환자에서 입원 중 PCSK9 inhibitor를 고강도 스타틴과 함께 투여하는 것이 안전하고 LDL을 효과적으로 감소시킨다는 Evolocumab for Early Reduction of LDL-Cholesterol Levels in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndromes (EVOPACS)가 European Society of Cardiology (ESC 2020)에서 발표되었다. 양군에서 모두 기저로 스타틴을 투여하고 있는 상황에서 PCSK9 inhibitor인 evolocumab (RepathaÒ) 사용군에서 8주후 평균 LDL이 77.1% 감소하였다 (위약군 35.4% 감소). 또한, evolocumab 사용군 대부분에서 치료 목표 [LDL <1.8 mmol/L (70 mg/dL)]에 도달하였지만 위약군은 37.6%만 도달하였다. 본 연구는 고위험 급성 ACS 환자에서 안정성 우려없이 획기적으로 LDL 감소를 증명한 스타틴과 evolocumab 병합 요법에 관한 첫 무작위, 이중맹검, phase III연구이다. 위약군과 evolocumab군에서 비슷한 모든 부작용 (50.7% vs 50.3%)과 심한 부작용(7.2% vs 7.7%)이 관찰되었고 evolocumab군에서 2명의 사망이 있었지만 약제와 관련은 없었다.
EVOPACS 연구자들은 308명의 급성기 ACS 환자를 1:1로 위약군 (고강도 statin + 위약)과 evolocumab (고강도 statin + evolocumab) 군으로 무작위 배정하였다. 대상군은 스타틴을 사용하지 않았던 경우 [LDL > 3.2 mmol/L (124mg/dL)], 저강도/중등도 스타틴 사용군 [LDL > 2.3 mmol/L (89mg/dL)], 또는 고강도 스타틴을 4주 이상 사용한 군 [LDL > 1.8 mmol/L (70mg/dL)]으로 구분되었다. 아토바스타틴 (리피토Ò) 40mg이상을 사용하면서 420mg evolocumab 이나 placebo를 입원 기간 중 및 4주후 투여하였다 (figure 1). 일차 종결점인 평균 LDL 감소는 위약군에서 3.42 mmol/L (기저)에서 2.06 mmol/L(8주)로 감소하였지만 evolocumab군에서 3.61 mmol/L 에서 0.79 mmol/L 로 현격하게 감소하였다 (figure 2, 3). 염증 인자인 hsCRP는 평균 6.6mg/dL(기저)에서 2.5mg/dL(8주)로 감소하였지만 양군에서 유의한 차이가 없었고 IL-6 및 IL-1β 도 차이가 없었다.
본 연구는 비교적 짧은 기간 동안 실시한 소규모 연구라는 제한점이 있지만 기존 대부분의 연구들이 급성기가 지난 안정된 환자를 대상으로 하였기 때문에 차별점이 있다. 따라서, 본 연구처럼 급성기 ACS 환자에서도 evolocumab을 통한 조기 LDL 감소가 가능하다면 향후 심혈관사건과의 연관이 있을지에 대한 추가 연구가 필요할 것이다.
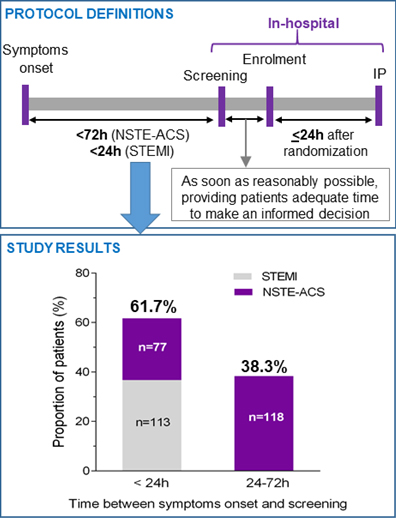
Figure 1. Upper panel: Protocol-defined time windows for enrolment and administration of the investigational product (IP) at baseline in relation to the time of onset of symptoms in patients presenting with acute coronary syndromes (ACS). Lower panel: shown are the proportions of patients who were screened for study enrolment within <24 hours or between 24 and 72 hours of symptoms onset, stratified by type of ASC (STEMI vs. NSTE-ACS).
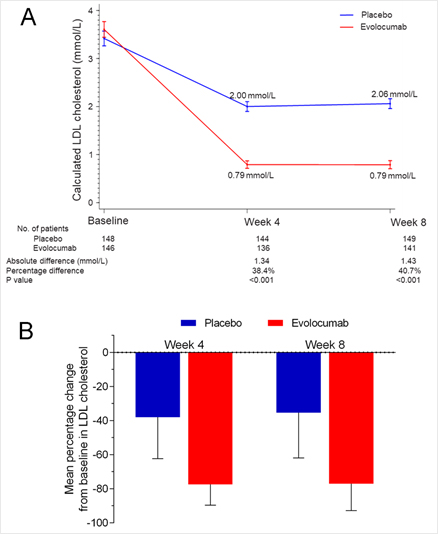
Figure 2. The change of calculated LDL cholesterol (A) and mean percentage change from baseline in LDL cholesterol (B).
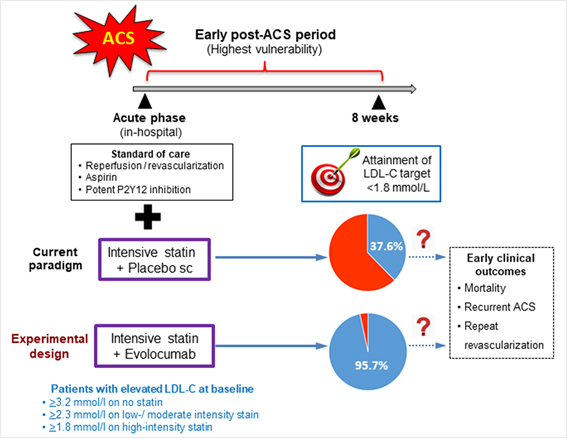
Figure 3. Evolocumab in patients with acute coronary syndrome.