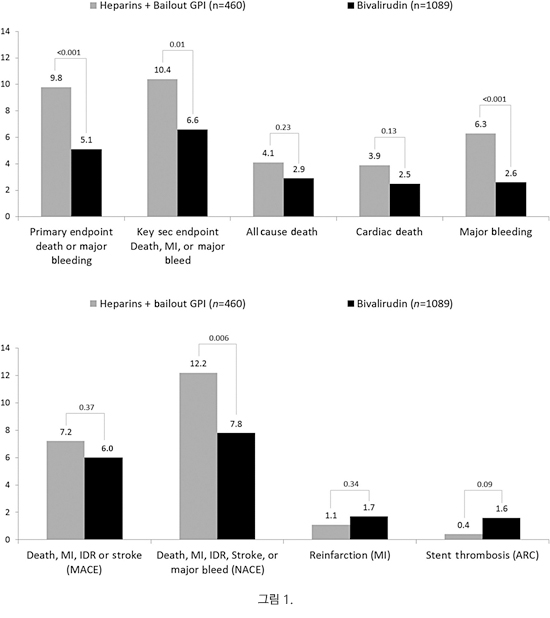
Acute coronary syndrome (ACS)은 stable disease에 비해 치명적인 임상경과를 보이므로 이를 정복하기 위해 많은 임상연구들이 집중되어 왔다. 그 성과로서 지난 수십년동안 항혈전요법과 중재시술의 괄목할 발전이 이루어져 왔고, 이는 임상결과의 향상으로 연결되어 생존율의 지속적인 개선이 이루어져 왔다. ACS의 발생기전에 있어 특히 혈전의 역할이 주요하기에 항혈전요법의 개선을 위한 모색은 계속되어 왔다. 다양한 antiplatelet agent들이 소개되어 사용 중이고, heparin 이후의 다양한 anticoagulant들도 출시되어 사용중인 상황에서 EUROMAX Trial (European Ambulance Acute Coronary Syndrome Angiography)의 결과가 보고되었다.1 Primary percutaneous coronary intervention (pPCI)으로 치료하기로 정해진 ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) 환자 2,218명을 pPCI 센터로 이송을 시작하는 단계에서 bivalirudin이나 heparin 투 여군으로 무작위 배정하여 치료를 시작한 후 결과를 본 연구이다. Primary outcome으로 설정된 사망과 major bleeding의 composite outcome은 bivalirudin 군에서 낮게 나왔으며 이는 사망률의 유의하지 않은 차이에도 불구하고 major bleeding의 유의한 차이에서 기인한 것으로 보인다. Stent thrombosis는 오히려 bivalirudin 군에서 높게 나온 것도 주지할 만 하다 (그림 1). Stent thrombosis에 대한 사후분석 결과에 의하면2 acute stent thrombosis (AST)는 극히 초기에 나타났으며 (median time=2.3h) pPCI 후에 bivalirudin을 low dose (0.25mg/kg/h)로 유지한 경우에만 heparin에 비해 빈발한 것으로 나타났고 (11 of 670 [1.6%] vs. 2 of 947 [0.2%]; p=0.008) high dose (1.75mg/kg/h)에서는 유의한 차이가 없었다 (1 of 244 [0.4%]; p=0.588). P2Y12 억제제의 종류에 따른 차이는 관찰되지 않았다. 이전에도 bivalirudin의 우세를 보고했던 비교 연구인 HORIZONS-AMI trial의 환자군과 EUROMAX trial의 환자군을 pooling하여 분석한 결과에서도 bivalirudin이 우월하다고 보고하고 있는 바 향후 heparin이 대체되는 흐름도 예상해 볼 수 있겠다.3
New generation drug-eluting stent (DES)의 삽입 이후에는 필수적인 dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT)의 기간도 짧으리라 예견되어 왔다. 최근 발표된 ITALIC trial의 결과에 의하면 Xience V DES가 삽입된 2,031명의 환자 중에서 DAPT를 12개월 유지한 군과 6개월 유지한 군에서 primary composite endpoint인 death, MI, TVR, stroke 및 major bleeding에 있어 유의한 차이를 보이지 않은 것으로 나타났으며 이는 연구에 포함된 44%의 ACS 환자들에서도 마찬가지였다.4 DES 삽입 이후 DAPT의 필수기간 단축도 기대가 된다.
중재시술 시 access site에 따른 결과의 차이에 대한 의문의 해답도 꾸준히 나오고 있다. 최근Transradial approach (TRA)가 transfemoral approach (TFA) 보다 access site 관련 합병증이 적다는 것에 대해 보편적인 공감이 형성되어 있는 가운데 BCIS (British Cardiovascular Intervention Society)의 자료를 분석한 최근의 보고는 주목할 만 하다.5
PCI가 시행된 439,947명의 환자를 stable disease, non-ST-segment elevation ACS (NSTEACS)와 ST-elevation ACS (STEACS)로 범주화하여 access site에 따라 비교분석을 한 결과 TRA가 TFA에 비해 모든 presenting syndrome에 걸쳐 출혈성 합병증이 적게 나타났고 (stable odds ratio [OR]: 0.24, p<0.001; NSTEACS OR: 0.35, p<0.001; STEACS OR: 0.47, p<0.001), access site 관련 합병증도 유의하게 적었다 (stable OR: 0.21, p<0.001; NSTEACS OR: 0.19; STEACS OR: 0.16, p<0.001). Unstable syndrome 환자군에서는 major adverse cardiac event도 TRA군에서 보다 적게 나타났다 (stable OR: 1.08, p=0.25; NSTEACS OR: 0.72, p<0.001; STEACS OR: 0.70, p<0.001). TFA에 closure device가 사용되었음에도 이러한 차이가 나타났으며, 대규모의 자료를 분석한 이 결과는 ACS에서의 TRA 이용에 더욱 힘을 실어줄 것으로 보인다.
References
1. Zeymer U, van 't Hof A, Adgey J et al. Bivalirudin is superior to heparins alone with bailout GP IIb/IIIa inhibitors in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction transported emergently for primary percutaneous coronary intervention: a pre-specified analysis from the EUROMAX trial. Eur Heart J. 2014;35:2460-2467.
2. Clemmensen P, Wiberg S, Van't Hof A et al. Acute Stent Thrombosis After Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: Insights From the EUROMAX Trial (European Ambulance Acute Coronary Syndrome Angiography). JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2015;8:214-220.
3. Stone GW, Mehran R, Goldstein P et al. Bivalirudin Versus Heparin With or Without Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa Inhibitors in Patients With STEMI Undergoing Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: Pooled Patient-Level Analysis From the HORIZONS-AMI and EUROMAX Trials. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;65:27-38.
4. Gilard M, Barragan P, Noryani AA et al. Six-month versus 24-month dual antiplatelet therapy after implantation of drug eluting stents in patients non-resistant to aspirin: ITALIC, a randomized multicenter trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014 Nov (in press).
5. Ratib K, Mamas MA, Anderson SG et al. Access site practice and procedural outcomes in relation to clinical presentation in 439,947 patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention in the United kingdom. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2015;8:20-29.